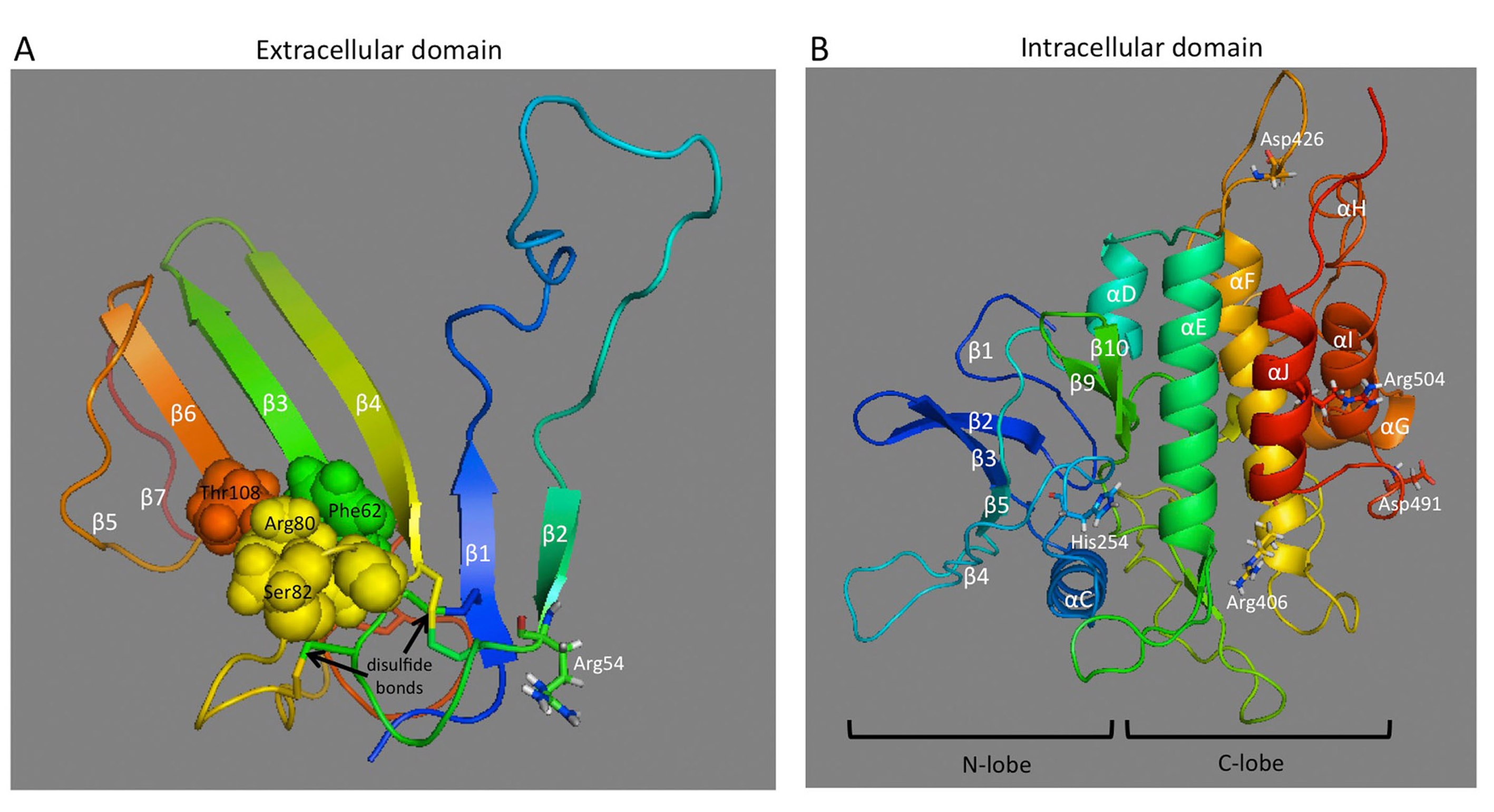
FIGURE 23. Molecular models of AMHR-II extracellular and intracellular domains.
(A) The extracellular domain exhibits the general three-finger toxin fold of type II receptors and displays five disulfide bridges, four of which are conserved in the other three receptors. Based on how the activin type II receptor interacts with BMP2, AMH may bind to an interface on the extracellular domain composed of residues Phe62, Arg80, Ser82, and Thr108, which are shown as spheres. (B) The intracellular domain exhibits the general fold of a two-domain kinase, with an N-lobe consisting mainly of a five-stranded β-sheet and a C-lobe, which is mainly α-helical. Residues affected by PMDS mutations (Arg54, His254, Arg406, Asp426, Asp491, and Arg504) are shown as sticks.
Reprinted with permission from Elsevier, from ref. 364: Josso N, Picard JY, Cate RL (2013). The Persistent Müllerian Duct Syndrome. In: New MI, Parsa A, Yuen TT, O’Malley BW, Hammer GD, eds. Genetic Steroid Disorders. New York, NY (USA): Elsevier.
