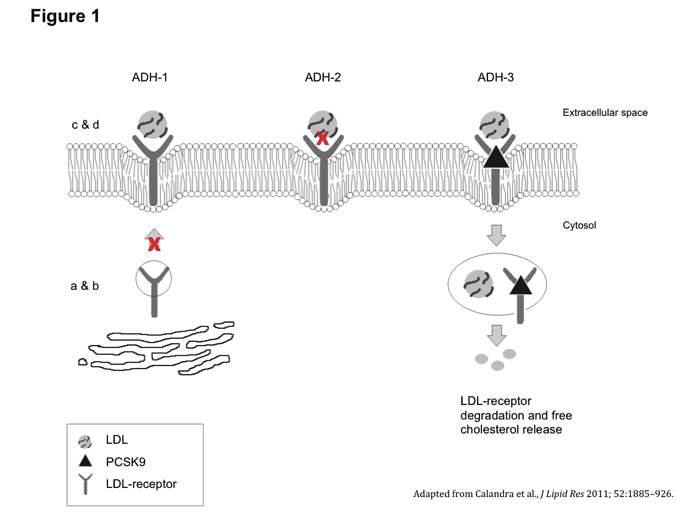
Figure 1: ADH can be classified into subtypes 1, 2, and 3, based on which protein of the LDLR pathway is affected. ADH-1 comprises mutations within LDLR. There are five major classes of ADH-1, affecting: 1) synthesis of LDLR; 2) exit of mature LDLR from the endoplasmic reticulum; 3) binding site of LDLR to apoB-100; 4) endocytosis of LDLR-apoB-100 complex; and recycling of LDLR to the cell surface (not shown). ADH-2 comprises mutations in apoB that block the association of apoB-100 to LDLR. ADH-3 is due to gain-of-function mutations of PCSK9, which reduce LDLR recycling and accelerate its lysosomal degradation
