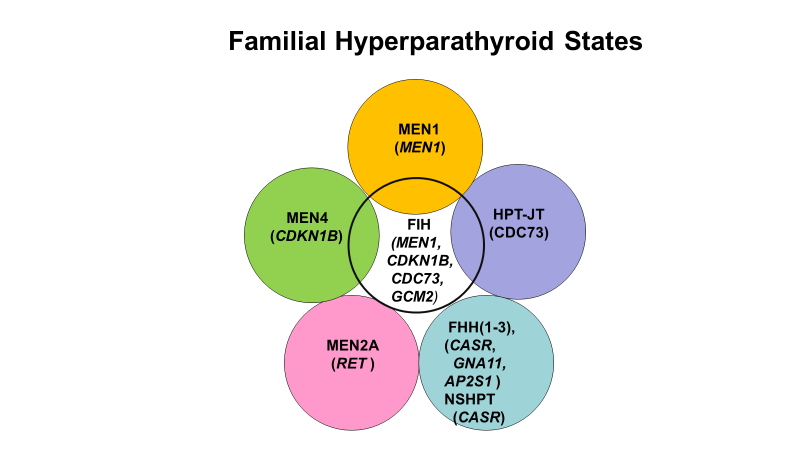
Figure 5. Familial hyperparathyroidism. Familial hyperparathyroidism (FHPT) can occur in the MENI Syndrome, in which MEN1 is mutated; in MEN4 in which CDKN1B is mutated; in the MEN2A Syndrome, in which RET is mutated; in FHH and NSHPT in which CaSR, GNA11 or AP2S1 is mutated; and in the Hyperparathyroidism-Jaw Tumor (HPT-JT) Syndrome in which CDC73 is mutated. Familial isolated hyperparathyroidism (FIH) refers to familial hyperparathyroidism in the absence of the specific features of the other documented syndromes and suggests that other genes relevant to parathyroid neoplasia await identification, although variants of several genes identified with syndromic FHPT have been found in some with this disorder.(eg MEN1, CDKN1B, CDC73, and GCM2).
